About Hybrin
Hybrin-General Information
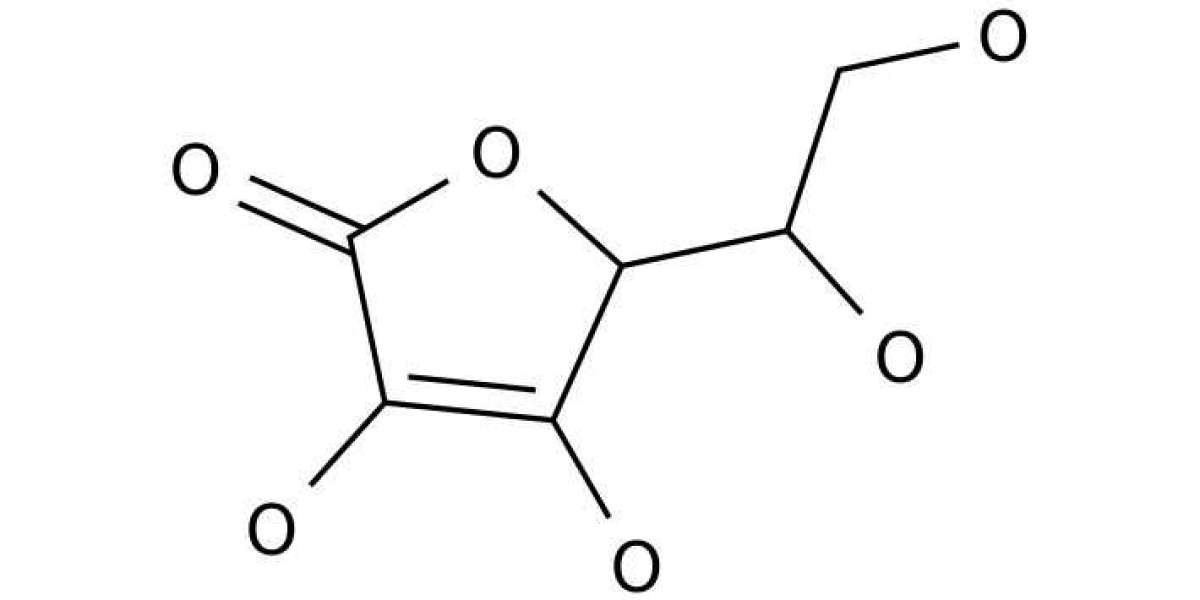
A 6-carbon compound related to glucose. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits and many vegetables. Ascorbic acid is an essential nutrient in the human diet and is required for the maintenance of connective tissue and bones. Its biologically active form, vitamin C, acts as a reducing agent and coenzyme in a variety of metabolic pathways. Hybrins are considered antioxidants.
Hybrin pharmacology
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is a water-soluble vitamin that can be used to prevent and treat scurvy because ascorbic acid deficiency causes scurvy. The structure of collagen is mainly affected, and lesions appear in bones and blood vessels. Taking ascorbic acid can completely relieve the symptoms of ascorbic acid deficiency.
Hybrin interaction
There is limited evidence that ascorbic acid can affect the strength and duration of action of dihydroxycoumarin. Indications for hibrin: For treatment of vitamin C deficiency, scurvy, delayed healing of wounds and bones, acidification of urine, often as an antioxidant. It is also considered a powerful antiviral agent.
Mechanism of action: In humans, exogenous ascorbic acid is required for collagen formation and tissue remodeling and functions as an adjunct to the post-translational formation of 4-hydroxyproline in the -Xaa-Pro-Gly- sequence of collagen and other proteins. Masu element. Ascorbic acid is reversibly oxidized in the body to dehydroascorbic acid. These two forms of vitamins are considered important in the redox reaction. Vitamins are involved in tyrosine metabolism, folic acid to folic acid conversion, carbohydrate metabolism, lipid and protein synthesis, iron metabolism, anti-infective disease, and cell respiration.