Market Overview
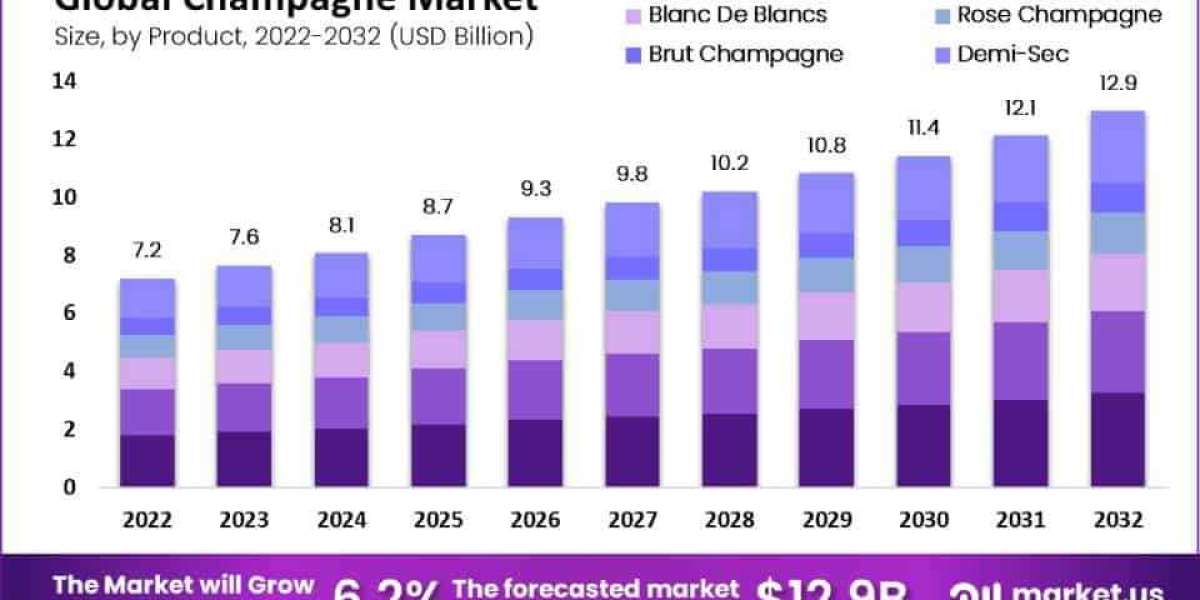
The Champagne Market size was estimated at USD 7.2 billion in 2022. The highest CAGR is estimated to be 6.2% in the period 2023 to 2032.
Champagne has a rich history that dates back centuries. The Champagne region in France is renowned for its unique terroir, which contributes to the distinct characteristics of Champagne wines. The region's winemaking traditions and expertise have been passed down through generations. Champagne is produced in various styles to suit different occasions and tastes. Non-vintage (NV) Champagne is the most common type, made by blending wines from multiple years to achieve consistency. Vintage Champagne is produced from grapes harvested in a single exceptional year, showcasing the unique characteristics of that specific vintage. Additionally, there are rosé Champagnes, blanc de blancs (made exclusively from Chardonnay grapes), and blanc de noirs (made exclusively from black-skinned grapes).
Top Key Players
- Moët Hennessy USA
- LANSON-BCC
- Vranken – Pommery Monopole
- Champagne Laurent-Perrier S.A.S.
- Pernod Ricard
- Rémy Cointreau
- The Centre Vinicole – Champagne Nicolas Feuillatte
- Martel
- Louis Roederer
- Taittinger
- Champagne Krug
- Other Key Players
Expert to drive your business success. Download our sample from https://market.us/report/champagne-market/request-sample/
Key Market Segments
Based on Product
- Prestige Cuvee
- Blanc De Noirs
- Blanc De Blancs
- Rose Champagne
- Brut Champagne
- Demi-Sec
Based on Distribution Channel
- On-Trade
- Off-Trade
The future of the Champagne market:
- Increasing global demand: As disposable incomes rise and consumer preferences shift towards premium products, the demand for Champagne is expected to increase. Emerging markets, such as China and India, are showing a growing interest in Champagne, contributing to its global demand.
- Diversification of offerings: Champagne producers are expanding their product portfolios to cater to a wider range of consumer preferences. This includes introducing new flavors, variations, and styles of Champagne to appeal to different tastes and occasions. Rosé Champagne, for example, has gained popularity in recent years.
- Sustainability and organic production: With increasing awareness about environmental issues, consumers are becoming more conscious of the sustainability and production practices of the products they consume. Champagne producers are adopting sustainable practices, such as organic and biodynamic farming, to meet this demand. This trend is likely to continue in the future.
- E-commerce and direct-to-consumer sales: The rise of e-commerce has transformed the way consumers purchase Champagne. Online platforms and direct-to-consumer sales allow Champagne producers to reach a wider audience and offer personalized experiences. This trend is expected to continue, especially with the convenience and accessibility it provides.
- Premiumization and exclusivity: Champagne is often associated with luxury and exclusivity. As consumers seek unique and premium experiences, there is a growing demand for high-end and limited-edition Champagnes. This trend is likely to continue, with Champagne houses creating special editions and collaborations to cater to this market segment.
The economic outlook for the Champagne market:
- Global Economic Recovery: The Champagne market, like many luxury goods sectors, was affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to disruptions in supply chains, reduced consumer spending, and restrictions on social gatherings. However, as economies recover and restrictions ease, there is an expectation of increased consumer confidence and a rebound in demand for Champagne.
- Consumer Spending and Disposable Income: The economic outlook for the Champagne market is closely tied to consumer spending and disposable income levels. Champagne is often associated with celebrations and special occasions, and consumer willingness to spend on luxury goods can influence the market's performance. Factors such as employment rates, wage growth, and overall economic stability can impact consumer spending patterns and, consequently, the demand for Champagne.
- International Trade and Tariffs: The Champagne market heavily relies on international trade, with significant exports to various countries. Changes in trade policies, tariffs, and geopolitical factors can affect the export and import dynamics of Champagne. Trade agreements and trade tensions between countries can impact the market's growth and profitability.
- Emerging Markets: The Champagne market has been experiencing growing demand from emerging markets, particularly in Asia, such as China and India. The economic growth and rising middle-class populations in these regions present opportunities for Champagne producers to expand their market reach. However, factors such as cultural preferences, import regulations, and economic stability in these markets can influence the market's growth potential.
- Competition from Sparkling Wines: While Champagne holds a prestigious position in the sparkling wine market, it faces competition from other sparkling wine regions, such as Prosecco from Italy and Cava from Spain. Consumer preferences and price sensitivity can impact the market share of Champagne compared to other sparkling wine options.
Supply chain analysis for the Champagne market:
- Grape Cultivation: The supply chain begins with grape cultivation in the Champagne region of France. Champagne grapes, including Chardonnay, Pinot Noir, and Pinot Meunier, are grown in vineyards across the region. Grape growers, known as viticulturists, play a crucial role in ensuring the quality and quantity of grapes produced.
- Harvesting and Sorting: Once the grapes reach optimal ripeness, they are harvested by hand. This labor-intensive process ensures that only the best grapes are selected. After harvesting, the grapes are sorted to remove any damaged or unripe grapes, ensuring that only high-quality grapes are used in Champagne production.
- Pressing and Fermentation: The sorted grapes are then gently pressed to extract the juice, which is the base for Champagne production. The juice undergoes primary fermentation, where yeast converts the sugars into alcohol. This process takes place in stainless steel tanks or oak barrels.
- Blending and Aging: After the primary fermentation, the winemaker blends different wines from different grape varieties and vintages to achieve the desired flavor profile and consistency. This blending process is a crucial step in Champagne production. The blended wine is then aged in cellars for a specific period, ranging from months to years, depending on the type of Champagne being produced.
- Secondary Fermentation: Once the desired aging period is complete, the winemaker adds a mixture of sugar and yeast, known as the liqueur de tirage, to the blended wine. This triggers a secondary fermentation process that takes place in the bottle. Carbon dioxide is trapped in the bottle, creating the characteristic bubbles of Champagne.
Contact us:
Global Business Development Team: Market.us
Market.us (Powered By Prudour Pvt. Ltd.)
Send Email: inquiry@market.us
Address: 420 Lexington Avenue, Suite 300 New York City, NY 10170, United States
Tel: +1 718 618 4351, +91 78878 22626